Introduction
The AI industry is predicted to witness significant expansion, going from a value of $81B in 2022 to an astonishing $909B by 2030. This growth is projected to occur at an impressive 35% CAGR between the years 2022 and 2030.
Today, out of the five forefront AI technologies gaining traction, generative AI, synonymous with "creation" in our AI value chain, exhibits the most rapid growth.
This high-level summary zeroes in on generative AI and provides a strategic framework for considering each element of the AI value chain.
Generative AI is poised to potentially disrupt businesses in every sector in the near future.
As the accuracy of generative AI improves alongside its ability to offer trustworthy factual counsel, its influence will permeate various sectors and business operations.
Applications span a wide spectrum, from customer assistance chatbots and production of news and marketing content, to code generation and product blueprinting.
Recommendations for management
Priority
Launch an internal process review to determine opportunities and risks of generative AI at process/task level (focus on tolerance for accuracy, need for factual advice, and product substitution potential)
High
Set company’s view on expected timeframe for i) accurate generative AI and ii) arrival of full substitutive AI (AGI)
Medium
Define full AI adoption strategy considering future scenarios (particularly i) and ii)
Medium
Define corporate policy to acquire generative AI capabilities (organic, partnership, off-the-shelf)
Medium
Understand regulatory framework particularly as it relates to data privacy and intellectual property ownership
High
Launch generative AI pilot projects to learn and understand technology
High
How much will the following technologies disrupt your industry?
During the first quarter of 2023, AI consistently retained its status as the technology regarded as the most transformative. This is a position it has successfully maintained since the third quarter of 2021.
Considerations for enterprise management

The allure of generative AI lies in its ability to tackle tasks that current AI applications have yet to master. Its capacity to write code, generate training data, and produce natural-sounding text opens up a world of unexplored possibilities across various industries.
When adopting generative AI, enterprises must carefully consider which model aligns best with their specific use case. They may need to employ multiple Language and Learning Models (LLMs) depending on their applications, and customization might be necessary to optimize the model for their specific needs.
To effectively incorporate generative AI into their operations, organizations should establish multi-disciplinary AI and Ethics teams. These teams can evaluate new AI use cases and ensure that they adhere to corporate ethical standards.
Human oversight should be a critical component of processes leveraging generative AI. Including human supervision at key stages ensures that outputs align with desired outcomes and ethical guidelines.
When evaluating generative AI solutions, organizations should prioritize model explainability. It is essential for users to understand the sources of information used to generate output and to assess their credibility.
Given the potential risks to individual privacy and unforeseen consequences, multiple countries are actively assessing the threats posed by generative AI. Organizations must navigate ethical and legal requirements at local, national, and international levels to ensure responsible and compliant AI practices.
Factors to Consider for IT Decision Makers
Enterprises exploring generative AI should consider multiple criteria when evaluating solutions
Brand reputation
Generative AI is already being made available via enterprise-grade platforms and tools by trusted technology partners, in response to the controversy and confusion swirling globally on the new technology’s trustworthiness. Customers are asking for 'chaperoned’' solutions that include guardrails offered by known brands.
Strength in security
Enterprises are concerned that their proprietary data will unintentionally end up in the public realm or be inadvertently used to train large language models, and therefore be accessible to others. Solution providers must ensure the security of enterprise data and customer information.
Ecosystem strength
Strong ecosystem partnerships between trusted technology providers (as mentioned) and advanced AI services by start-ups/pure plays with important innovations are all part of a trusted and cohesive partner program backed by leading cloud platform providers, global SIs, and SPs. Solutions that provide a seamless, end-to-end user experience and easily integrate with an enterprise’s existing IT environment will facilitate the adoption of generative AI.
Explainability
Explainable AI, such as understanding the sources used to produce generative AI content, is essential for enterprises to trust model results and take meaningful action based on findings.
Advanced data architecture
Data management capabilities, such as data fabrics and other solutions, that reduce data silos and streamline access to information across data repositories, provide a more efficient and consistent experience to data professionals involved in deploying advanced analytics projects.
Go-to-market strategy and professional services
A vendor with a strong base of reference customers, and pricing models that address flexible consumption are critical to new users. At the same time, deploying a generative AI solution can be a complex task, even for organizations with extensive in-house resources. Buyers should look for providers that have a team of experts available to help them navigate the process.
Performance
As the market evolves and organizations begin to rely on generative AI, they will look for solutions that consistently demonstrate low latency and reliability, produce diverse results, successfully preserve meaning and intent, secure enterprise data, and offer filters that act as guardrails.
Key phases in the development of generative AI
Generative AI: Overview
Generative AI is a type of foundational AI technology that uses machine learning algorithms to create content, including text, images, audio, video, speech, design, and software code
Large language models (LLMs) can generate many types of content
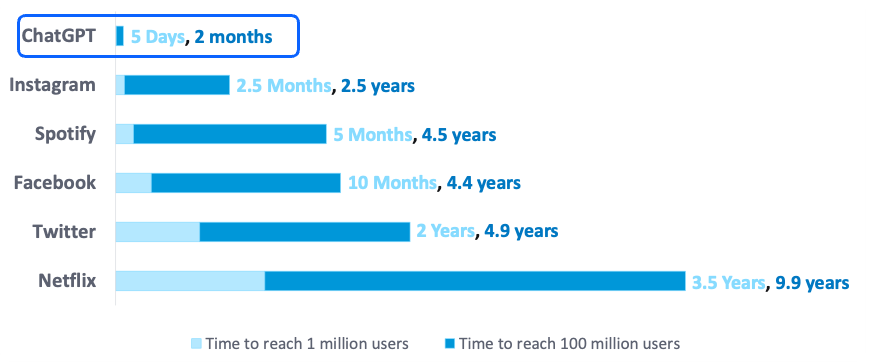
Generative AI has grown faster than any other technology
Until recently, ChatGPT was the first to reach one million and 100 million users
Generative AI refers to a category of artificial intelligence techniques and algorithms that are designed to generate new data or content that is similar to what it has been trained on. This can include text, images, videos, music, and other types of content. Examples of generative AI include image and video synthesis, text generation, music composition etc.
Patent filing trends in generative AI
83% CAGR in last five years
US leads the race, followed by China and Europe
Adoption trends are exploding
How did we go from linear regression to creation?
Three important developments led us here:
The Transformer deep learning model
The Transformer deep learning model was designed by a team at Google in 2017. It addressed two key limitations of prior deep learning models for language:
The lack of parallelism, or the ability to compute multiple parts of a deep learning model simultaneously
Determining which words in the original sentence are more relevant
Advances in AI chips
AI chips have been optimized in a few areas including memory and parallelism.
This has materially sped up deep learning model computations, allowing for AI creativity
The phenomenon of ‘emerging abilities’
These are new abilities that the model has not been specifically trained to do.
These only emerge in larger models.
We do not know how they emerge so cannot be predicted or controlled.
Advanced AI capabilities
There are five advanced AI capabilities; Creation, or Generative AI, is one of them
Full AI value chain
Where does generative AI (or creation) fall within the AI value chain?
Significant open questions indicate that generative AI has an unclear roadmap
The outcome of these questions will determine the long-term impact on businesses investment decisions
Key phases in the development of generative AI
AI corporate response framework
This framework sets out what you should do, based on how generative AI could impact your business
The urgency of your response depends on what type of generative AI is required for your business: Basic (available now), Greater accuracy (1-5 years), Knowledgeable (10-30 years), or Conscious (35-100 years)
When the impact is only in the Knowledgeable and Conscious phases, you need to form a view on the open industry debates (will scaling and emerging abilities lead to Knowledgeable or Conscious generative AI?)
Generative AI business process use cases
Roadmap Across Selected Sectors
Key takeaways
While much of the hype around generative AI today centers on the technology’s ability to create textual content, generative AI can produce a range of output, including images, video, code, and speech/audio.
Business transformation efforts are demanding intelligent chatbots and other generative AI integrations to move up the development stack and enhance customers’ image, video, and audio experiences
DevOps teams can use the technology to support app modernization and business transformations, using ChatGPT to write or convert new code and scripts.
Numerous players participate in the generative AI market, ranging from large hyperscale cloud providers such as Microsoft, Google, and Baidu, to niche providers such as Anthropic, Cohere, and Hugging Face.
Enterprises should consider multiple buying criteria when selecting a vendor, such as brand reputation, ecosystem strength, explainability, go-to-market strategy, and performance.
When adopting generative AI, enterprises face additional hurdles beyond those encountered with traditional AI deployments, especially in the realm of responsible AI and ethics.
AI market drivers
Staving off commoditization
Cloud giants want to attract low-coders and non-coders to their respective platforms e.g., Azure, AWS, GCP.
Advanced AI services can eliminate complex baseline coding requirements.
AI-injected Apps
Providers are operationalizing generative AI for use within bespoke applications.
Business transformation efforts are demanding generative AI integrations to move up the development stack and enhance customers’ image, video, and audio experiences.
Citizen data scientists
At a time when the industry is experiencing a global technology skills gap, tools based on AI, low-code platforms, and automation are more relevant than ever.
Companies scrambling to reskill internal personnel are seeking out relevant tools including GitHub Copilot for abstracting time-consuming tasks such as baseline coding.
Generative AI will significantly bypass similar levels of complexity.
Consumer momentum
The ease with which individuals can use ChatGPT has propelled generative AI into the headlines and onto the agendas of non-technical business leaders.
It has stirred up widespread public interest in the technology and driven extensive curiosity into potential business applications.
Operational efficiency
Years of investment in deep learning, NLP, and LLM, have been enabled through increasingly powerful computing frameworks and algorithms.
Generative AI is poised to enhance intelligent automation solutions, alongside app deployments, networking, coding, security, etc.
Provider Profiles
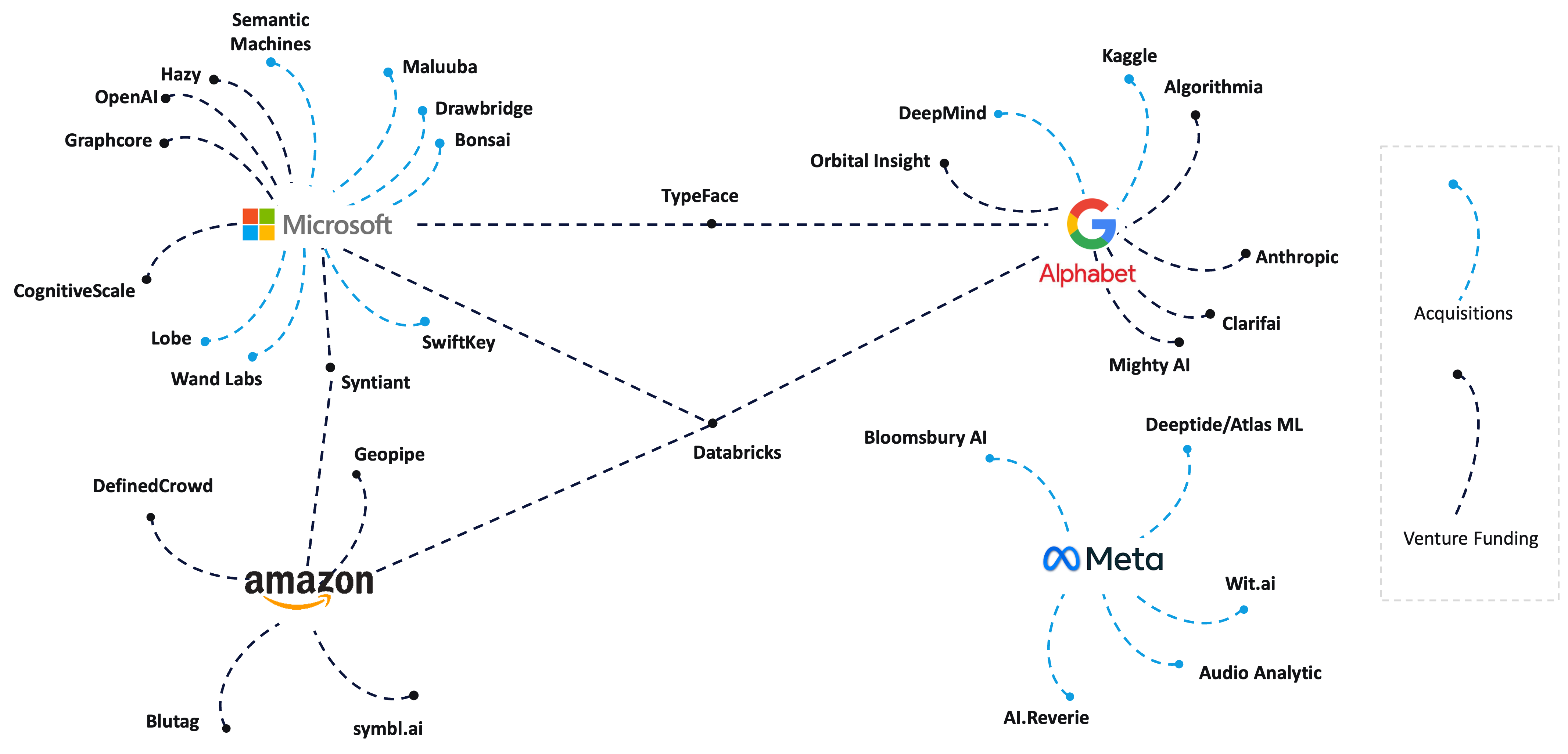
Strategic partnerships and collaborations across the generative AI tech stack
Big Tech complements their generative AI tech stack presence through strategic alliances, predominantly with start-ups and a few within them
Notable venture financing and acquisitions
MAGMA, particularly Google and Microsoft, are highly active in funding and acquiring companies with generative AI capabilities.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Curious Compass to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.